The Nikon D200 User Guide serves as your comprehensive companion to unlocking the full potential of this powerful DSLR. This guide will navigate you through the intricacies of the D200, from its initial setup to mastering advanced techniques. Whether you’re a seasoned photographer seeking to refine your craft or a novice eager to explore the world of digital photography, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to capture stunning images.
The Nikon D200, released in 2005, was a game-changer in the world of digital SLR cameras. It boasted a 10.2-megapixel sensor, a robust build, and a plethora of features that made it a favorite among professionals and enthusiasts alike. Its ability to capture high-quality images with excellent detail and dynamic range, coupled with its versatility and user-friendliness, cemented its place as a highly sought-after camera in the market.
Flash Photography
The Nikon D200’s built-in flash is a valuable tool for capturing well-lit images in challenging situations. It allows you to freeze action, illuminate subjects in low light, and add a touch of creative flair to your photographs. Understanding the flash system and its various settings will enable you to utilize it effectively and achieve stunning results.
Built-in Flash Modes and Features
The D200’s built-in flash offers a range of modes to suit different photographic needs. The modes provide control over the flash’s output and behavior, allowing you to achieve the desired lighting effect.
The Nikon D200 user guide is a valuable resource for mastering the camera’s intricate features, from its robust autofocus system to its powerful image processing engine. For those seeking a more classic approach to photography, the Leica R50 might be a tempting alternative.
However, choosing between the Leica R50 v1 and v2 can be a dilemma, as each version boasts unique strengths. A detailed comparison of the Leica R50 v1 and v2 reveals key differences in their metering systems and lens compatibility, which can significantly impact the user experience.
Returning to the Nikon D200, its user guide provides comprehensive insights into its advanced capabilities, ensuring that photographers can fully harness its potential.
- Auto Mode:The camera automatically determines the flash intensity based on the scene’s lighting conditions. This is the simplest mode, ideal for general use.
- Fill-in Mode:The flash provides a burst of light to fill in shadows, creating a more balanced exposure, particularly in bright sunlight.
- Red-eye Reduction Mode:This mode emits a pre-flash to minimize the red-eye effect, which occurs when the flash reflects off the retina of the subject’s eyes.
- Slow Synchro Mode:This mode allows the flash to fire at the beginning of a long exposure, resulting in a background that is blurred while the subject remains sharp. This mode is particularly useful for capturing motion blur in low-light environments.
- Rear Curtain Sync Mode:In this mode, the flash fires at the end of a long exposure, allowing the subject to appear as a streak of light against a sharp background.
Using External Flash Units
While the D200’s built-in flash is capable, using an external flash unit offers greater flexibility and control. External flashes provide more powerful illumination, allowing you to illuminate subjects from a distance and achieve a wider range of lighting effects.
The Nikon D200 user guide, a treasure trove of technical details and shooting tips, can help you unlock the full potential of this powerful DSLR. Whether you’re a seasoned photographer or just starting out, understanding the camera’s features is key to capturing stunning images.
For those seeking the ultimate travel companion, consider consulting our guide on the best camera for travel to find the perfect fit for your adventures. Armed with this knowledge, you’ll be well-equipped to use the Nikon D200 to document your journeys with clarity and precision.
- Increased Power:External flashes typically offer greater power output than built-in flashes, enabling you to illuminate subjects farther away or in darker environments.
- Bounce Flash:External flashes can be detached from the camera and directed towards a reflective surface, such as a wall or ceiling. This technique softens the light, creating a more natural and flattering effect.
- Creative Lighting:External flashes allow you to experiment with different lighting angles and techniques, creating dramatic shadows and highlighting specific areas of your subjects.
- Wireless Control:Some external flashes can be triggered wirelessly, allowing you to place them off-camera for greater creative control.
Tips for Effective Flash Photography
Mastering flash photography requires understanding how to control the flash’s power, use bounce flash effectively, and avoid red-eye.
- Controlling Flash Power:The flash’s power output can be adjusted to match the lighting conditions and subject distance. Reducing the flash power can soften the light and create a more natural effect, while increasing the power can illuminate subjects farther away.
- Bounce Flash:Bouncing the flash off a reflective surface softens the light, creating a more natural and pleasing effect. This technique reduces harsh shadows and eliminates the direct, “flash-like” look.
- Avoiding Red-eye:The red-eye effect can be minimized by using the red-eye reduction mode, having the subject look slightly away from the camera, or using a diffuser to soften the flash light.
- Flash Exposure Compensation:The flash exposure compensation setting allows you to fine-tune the flash’s output, adjusting the overall brightness of the subject. This is particularly useful when shooting in challenging lighting conditions.
Advanced Features and Settings
The Nikon D200 offers a suite of advanced features designed to empower photographers to control every aspect of their images. These features extend beyond basic settings, allowing for creative customization and precise image manipulation.
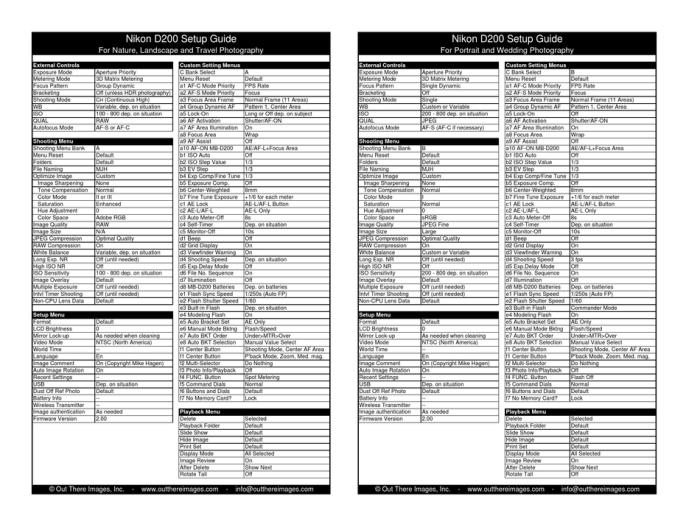
Custom Settings
Custom settings allow photographers to tailor the camera’s behavior to their specific shooting preferences and workflow. This includes assigning specific functions to buttons, adjusting exposure compensation, and customizing the camera’s display.
The Nikon D200 user guide is a valuable resource for photographers, offering a comprehensive overview of its features and capabilities. From understanding the intricacies of its autofocus system to mastering the nuances of its manual controls, the guide empowers users to unlock the full potential of this iconic camera.
However, the post-processing workflow is just as crucial, and the choice between Affinity Photo and Lightroom can significantly impact your final results. Affinity Photo vs Lightroom presents a detailed comparison of these two popular photo editing software, helping you decide which best suits your needs and preferences.
Armed with the knowledge from both the Nikon D200 user guide and a well-informed software selection, you can confidently navigate the exciting world of digital photography.
- Custom Settings Menu:The D200’s Custom Settings menu provides a comprehensive range of options to personalize the camera’s operation. This menu is accessed by pressing the “Menu” button and navigating to the “Custom Setting” tab.
- Custom Settings Banks:The camera allows you to store multiple custom settings configurations, enabling quick switching between different shooting styles. For example, one bank could be configured for landscape photography, while another could be optimized for sports.
- Custom Function (Fn) Buttons:The D200 features dedicated Fn buttons that can be assigned to frequently used functions, such as ISO sensitivity, white balance, or metering mode. This allows for quick access to essential settings during a shoot.
Picture Styles
Picture Styles are pre-defined settings that affect the overall look and feel of images by adjusting parameters like sharpness, contrast, and saturation. These styles provide a starting point for different photographic genres or personal preferences.
- Standard:A balanced setting that delivers a neutral image suitable for various subjects and situations.
- Neutral:Produces a more muted image with reduced contrast and saturation, ideal for post-processing and fine-tuning.
- Vivid:Enhances colors and contrast for a more vibrant and dramatic image, often preferred for landscapes and portraits.
- Monotone:Creates black and white images with various tonal adjustments for artistic expression.
- Portrait:Emphasizes skin tones and softens highlights for flattering portraits.
- Landscape:Enhances sharpness and contrast for detailed and impactful landscapes.
In-Camera Editing
The D200 offers basic in-camera editing capabilities, allowing photographers to make minor adjustments to their images before transferring them to a computer.
- Image Retouch:This function allows for basic adjustments to brightness, contrast, and color balance. It also provides options for cropping and resizing images.
- Red-Eye Correction:The camera can automatically detect and correct red-eye in portraits, a common issue with flash photography.
- Image Overlay:The D200 allows for the overlay of two images, enabling the creation of composite images or special effects.
Bracketing
Bracketing is a technique that captures multiple images of the same scene with slight variations in exposure, focus, or white balance. This allows photographers to choose the best image or combine multiple exposures for greater dynamic range and detail.
The Nikon D200 user guide is a valuable resource for anyone seeking to master the intricacies of this popular DSLR. Understanding the D200’s capabilities, from its robust autofocus system to its high-resolution sensor, can be greatly enhanced by studying the guide.
For those interested in compact camera alternatives, the Sony RX100 series offers a compelling option. A comparison between the rx100 ii vs rx100 iii reveals significant advancements in image quality and performance, showcasing the evolution of compact camera technology.
However, returning to the D200 user guide, we find a wealth of knowledge about the camera’s advanced features, such as its custom settings and image processing options, allowing photographers to achieve their desired results.
- Exposure Bracketing:Captures a series of images with different exposure values, allowing for a wider range of tonal detail in high-contrast scenes.
- Focus Bracketing:Takes multiple images with varying focus points, ensuring sharp focus across a wider area, especially useful for macro photography.
- White Balance Bracketing:Captures images with different white balance settings, allowing for flexibility in post-processing and accurate color reproduction under various lighting conditions.
Customizing Camera Settings
The D200 provides numerous settings that can be customized to optimize performance for specific shooting situations.
- ISO Sensitivity:Adjusts the camera’s sensitivity to light, allowing for faster shutter speeds in low-light conditions. However, higher ISO settings can introduce noise in the image.
- Metering Mode:Determines how the camera measures the overall brightness of the scene and sets exposure accordingly. Different metering modes are suited for various subjects and lighting conditions.
- Focus Mode:Controls how the camera focuses on the subject, ranging from single-point autofocus to continuous autofocus for moving subjects.
- Image Quality:Allows selection of different image file formats and resolutions, balancing file size and image quality.
- White Balance:Adjusts the color temperature of the image to compensate for different light sources and ensure accurate color reproduction.
Connectivity and Data Management: Nikon D200 User Guide
The Nikon D200 offers a range of connectivity options for transferring images and connecting to external devices. Understanding these options and mastering data management techniques will ensure efficient workflow and seamless integration with your digital imaging process.
Connecting the Nikon D200
The Nikon D200 offers several methods for connecting to external devices. The primary options include:
- USB Connection:The USB port on the camera provides a versatile connection for transferring images to a computer or other devices. It supports both USB 1.1 and USB 2.0 standards, enabling high-speed data transfer.
- HDMI Connection:The HDMI port allows for direct connection to an HDTV or monitor, enabling you to view high-resolution images and videos on a larger screen. The HDMI port supports the latest standards, ensuring optimal image quality and clarity.
- Remote Control:The Nikon D200 can be controlled remotely using a dedicated remote control unit or compatible software. This functionality allows for hands-free operation, particularly useful in scenarios where direct access to the camera is limited.
Transferring Images
Transferring images from the Nikon D200 to a computer or other devices is a straightforward process. The camera provides several options:
- Direct Transfer via USB:Using a USB cable, connect the camera to your computer. The camera will appear as a removable drive, allowing you to access and copy images directly to your computer.
- Wireless Transfer:The Nikon D200 does not have built-in Wi-Fi capability. However, you can utilize a wireless adapter, such as the Nikon WU-1a Wireless Mobile Adapter, to transfer images wirelessly to your smartphone or tablet.
- Memory Card Reader:Alternatively, you can use a memory card reader to transfer images from the camera’s SD card to your computer. Memory card readers are widely available and offer a convenient and fast method for transferring images.
Organizing and Managing Images
Effective image organization and management are crucial for efficient workflow and easy access to your photographs. Here are some tips for managing your images effectively:
- Create a Consistent File Naming System:Implementing a consistent file naming system, such as using a date-based structure (e.g., YYYYMMDD_ImageDescription), will help you organize and locate images easily.
- Utilize Folders and Subfolders:Create folders and subfolders based on specific criteria, such as event, location, or subject matter. This hierarchical structure allows for easy navigation and retrieval of images.
- Utilize Image Management Software:Dedicated image management software, such as Adobe Lightroom or Capture One, offers advanced features for organizing, editing, and cataloging your images. These programs allow for tagging, rating systems, and other features that enhance image management.
- Regular Backups:It is crucial to regularly back up your images to prevent data loss. Consider multiple backup strategies, such as using external hard drives, cloud storage services, or a combination of both.
Conclusion

This user guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the Nikon D200’s capabilities, encompassing fundamental operations, advanced settings, and specialized techniques. You’ve learned about the camera’s core functionalities, such as exposure control, autofocus, and image composition, as well as its powerful features for creative expression, including flash photography, custom settings, and data management.
Maximizing the D200’s Potential
The Nikon D200 is a versatile camera designed to empower photographers of all levels. By understanding its features and techniques, you can capture stunning images in various scenarios.
“The key to unlocking the D200’s potential lies in continuous exploration and experimentation.”
Resources for Continued Learning, Nikon d200 user guide
The journey of photography is a lifelong pursuit of knowledge and skill. To further enhance your photographic skills, explore the following resources:
- Nikon’s official website:Offers comprehensive manuals, tutorials, and support resources for the D200.
- Online photography communities and forums:Connect with other photographers, share experiences, and learn from their insights.
- Photography books and magazines:Provide in-depth knowledge on various photographic techniques, genres, and equipment.
- Photography workshops and classes:Offer hands-on learning experiences with experienced instructors.
Concluding Remarks

As you delve deeper into the world of the Nikon D200, remember that practice is key to mastering its capabilities. Experiment with different settings, explore various shooting techniques, and don’t hesitate to push the boundaries of your creativity. With the knowledge gained from this guide and your own dedication, you’ll be well on your way to capturing breathtaking photographs that tell stories and evoke emotions.